The world of options trading offers a myriad of strategies to capitalize on market movements, each with its unique characteristics and risk profiles.
Among these strategies is the short straddle strategy, a popular approach that allows traders to profit from minimal market movement.
In this guide, we’ll delve into what a short straddle entails, its application in the context of the Nifty 50 index, as well as its merits, demerits, and ideal scenarios for implementation.
In my next blog, I’ll talk about 5 to 6 advanced adjustments for trading strategies, also called firefighting. These adjustments help handle unexpected challenges in trading.
They work for all kinds of strategies, making them better suited for changing market conditions. Stay tuned to learn more about improving your trading game!
What is a Short Straddle?
A short straddle is an options trading strategy where a trader simultaneously sells a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
By executing this strategy, the trader believes that the underlying asset’s price will remain relatively stable, thus profiting from the decay of the options’ time value.
Implementation of the Short Straddle Strategy
1. Identify Suitable Underlying Asset:
Choose a stock or index with relatively low volatility and stable price movement.
2. Select Strike Price and Expiration Date:
Opt for the at-the-money (ATM) strike price and an expiration date that aligns with your trading horizon.
3. Sell Call and Put Options:
Execute the short straddle by simultaneously selling a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
4. Receive Premium:
As the seller of the options, you’ll receive a premium, which represents your maximum potential profit.
Potential Outcomes of a Short Straddle
1. Maximum Profit:
The maximum profit is achieved when both options expire worthless. It equals the premium received from selling the options.
2. Breakeven Points:
There are two breakeven points for the short straddle:
- Upper Breakeven: Strike price + Premium received
- Lower Breakeven: Strike price – Premium received
3. Maximum Loss:
Unlimited potential loss exists if the underlying asset experiences a significant price movement in either direction.
The loss equals the difference between the strike price and the actual price of the underlying asset, plus the premium received.
This is a high risk strategy. Its always good to buy hedges to overcome losses from unforeseen events.
Example of Short Straddle Strategy with Nifty50
Let’s illustrate the short straddle strategy with an example using options on the Nifty50 index, which represents the performance of the top 50 companies listed on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE).
For simplicity, we’ll consider hypothetical prices and dates.
Scenario:
- Nifty50 Index is currently trading around at 22,500.
- Options expiration date is one month away.
- Volatility is relatively low, indicating stable market conditions.
Implementation:
1. Identify Suitable Underlying Asset:
We choose the Nifty50 index, which is widely traded and has relatively stable price movement.
2. Select Strike Price and Expiration Date:
With Nifty50 trading at 22,500, we select the at-the-money (ATM) strike price of 22,500 for both the call and put options. We choose an expiration date one month away to align with our trading horizon.
3. Sell Call and Put Options:
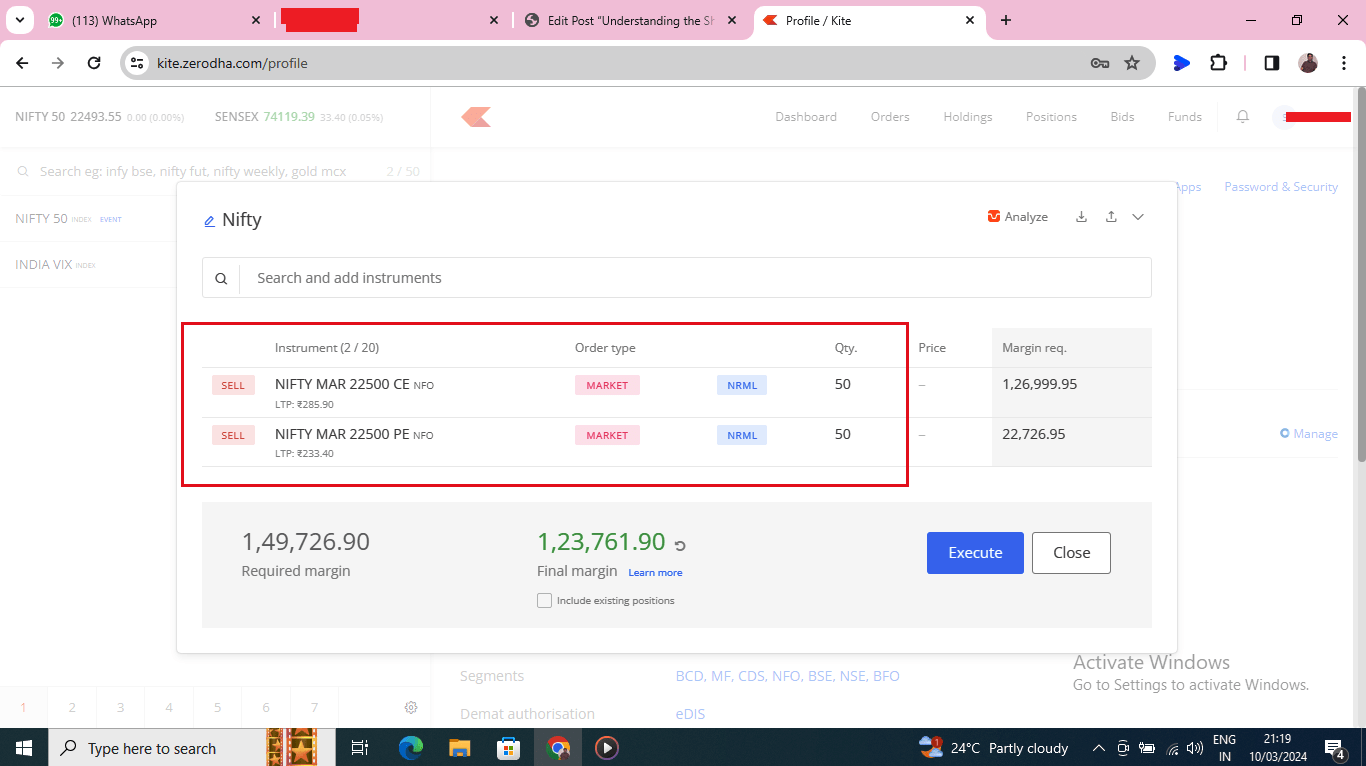
We execute the short straddle by simultaneously selling:
- 1 Nifty50 call option with a strike price of 22,500
- 1 Nifty50 put option with a strike price of 22,500
4. Receive Premium:
As the seller of both options, we receive a premium.
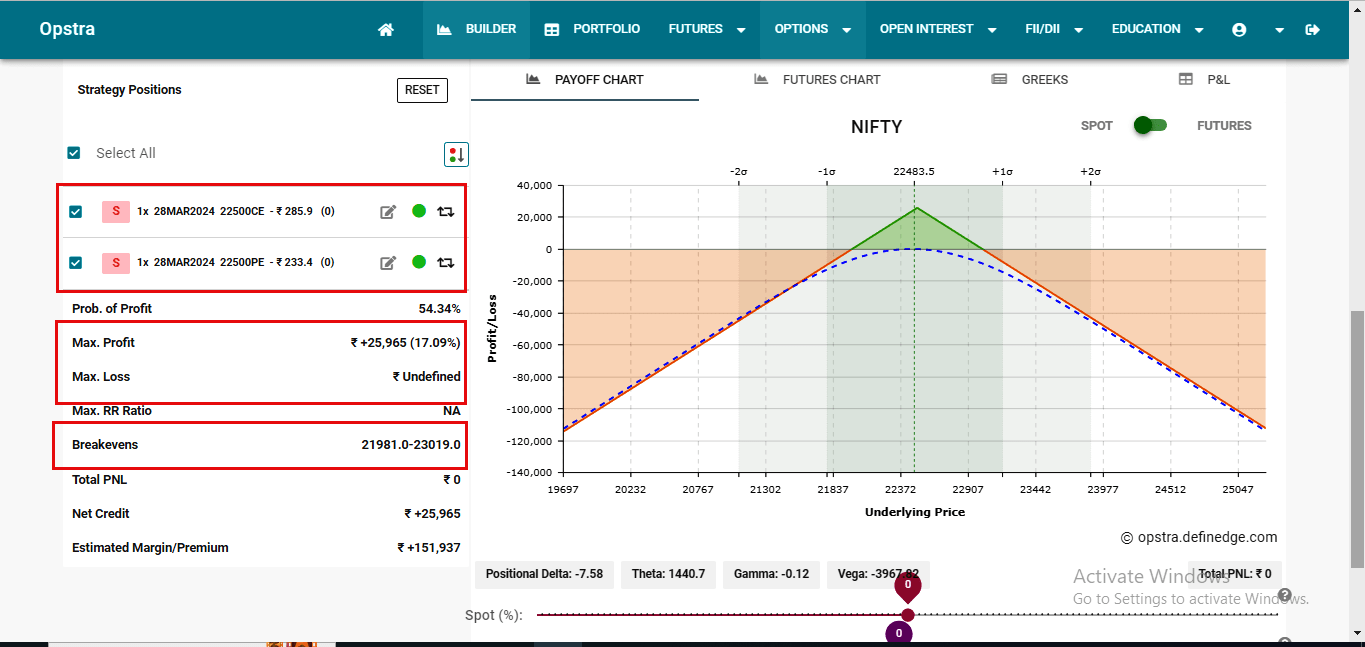
- Premium received for selling the Call Option (CE): ₹ 285.9
- Premium received for selling the Put Option (PE): ₹ 233.4
- Total Premium Recived: ₹ 286 + ₹ 233 = ₹ 519.3
Potential Outcomes:
1. Maximum Profit:
If Nifty 50 remains near the 22,500 strike price at expiration, both the call and put options will expire worthless, allowing us to keep the entire premium received (₹ 519.3 * 50 {lot size}= Rs. 25965 ) as our maximum profit.
2. Breakeven Points:
- Upper Breakeven: 22,500 (strike price) + 519.3 (premium received) = 23019
- Lower Breakeven: 22,500 (strike price) – 519.3 (premium received) = 21981
- If Nifty50 expires between 21981-23019 then there will be profit, but if it closes beyond the range then there will be loss depending upon the close of Nifty50.
3. Maximum Loss:
Unlimited potential loss occurs if Nifty50 experiences a significant price movement in either direction.
For example, if Nifty50 rallies to 23,500 our maximum loss would be:
Loss from the short call option: = (Current price of Nifty50 – Strike price of call option) – Call premium * Lot size
= (23,500 – 22,500) – 285.9 * 50 = -₹35,705 (negative because it’s a loss)
Profit from the short put option: As the put option expires out of the money, its value becomes zero, resulting in a profit equal to the premium received.
= Put premium * Lot size = 233.4 * 50 = ₹11,670
Total Loss = Profit from short put option – Loss from short call option
= ₹11,670 – ₹35,705 = -₹24,035
So, the loss in this scenario would be -₹24,035.
If the Nifty 50 were to move even further, say to 24,000 or higher, the loss from the short call option would increase, thereby increasing the total loss.
Merits and Demerits of the Short Straddle Strategy
Merits:
1. Profit from Low Volatility:
Short straddles thrive in low-volatility environments, where the decay of option premiums works in the trader’s favor.
2. Income Generation:
The initial credit received from selling the options provides an immediate income stream for the trader.
Demerits:
1. Unlimited Risk:
In theory, the losses in a short straddle strategy can be unlimited if the underlying asset’s price makes a significant move.
2. Margin Requirements:
Brokers may require substantial margin to execute a short straddle due to the unlimited risk involved.
3. Potential Losses During High Volatility:
If the underlying asset experiences significant price movements, it can result in substantial losses for the trader.
When to Use the Short Straddle Strategy
Traders often employ the short straddle strategy in anticipation of low volatility or when they believe that the underlying asset will trade within a narrow range until the options expire.
Additionally, it can be used to profit from time decay, as options lose value as they approach expiration.
It’s typically employed in low-volatility environments or during periods of consolidation when the market is range-bound.
Additionally, traders should have a thorough understanding of options trading and risk management before employing this strategy due to its unlimited risk potential.
Key Takeaways
– The short straddle involves simultaneously selling a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date, banking on minimal market movement.
– Choose a stable underlying asset, opt for an at-the-money strike price, and execute both options together to receive a premium.
– Maximum profit occurs if the underlying asset remains close to the strike price at expiration. Breakeven points are determined by adding or subtracting the premium from the strike price. Losses can be unlimited if the asset’s price moves significantly.
– Benefits include profiting from low volatility and generating immediate income through option premiums.
– Drawbacks include the potential for unlimited losses, high margin requirements, and susceptibility to substantial losses during periods of high volatility.
Conclusion :
While the strategy offers the potential for profit in neutral market conditions, it carries the risk of unlimited losses if the underlying asset experiences significant price movement.
Traders should carefully assess market conditions, employ proper risk management techniques, and continuously monitor their positions when executing the short straddle strategy.
Disclaimer : The information provided in this post is for educational and informational purposes only. It should not be considered as financial advice. Investing in the stock market involves risks, and individuals should conduct their own research or consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions. The blog author and publisher do not guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the information provided, and shall not be held liable for any losses or damages arising from the use of this information.